Wiping Options
By default, wiping tasks are executed with the options recommended by the Jetico team. You can change the default settings in the ‘Wiping options’ section when creating a new task.
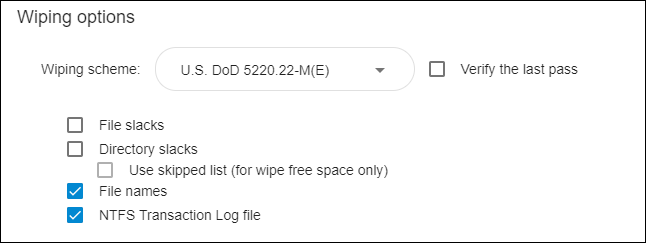
The following options are available:
‘Wiping scheme’: Select a wiping scheme from the drop-down menu.
‘Verify last pass’: Tick this checkbox to enable verification.
🗲HINT: The wiping schemes offered in BCWipe include detailed specifications, security levels, and Jetico’s selections for different drive types. The full list of wiping schemes is available here: Wiping Schemes in BCWipe
🗹 File slacks — Select this option to erase traces of previously deleted files from file slacks.
File slacks are the disk space between the end of a file and the end of the last cluster occupied by the file. Some parts of files that were deleted without wiping might get trapped in slacks of existing files and can potentially be recovered.
🗲HINT: When ‘File slacks’ is enabled in combination with the ‘Wipe user activity’, ‘Wipe browser history’, and ‘Delete with wiping’ commands, only the file slacks of the files that are being wiped will be erased. To erase file slacks for every file on a drive, enable the ‘Wipe free space’ command for that drive.
🗹 Directory slacks — Select this option to erase file names, attributes, and traces of previously deleted files from directory slacks.
- For NTFS drives: NTFS directory is a special file that contains the names of files and subdirectories. The disk cluster that belongs to a directory is called a directory node. Directory nodes contain a file slack, which is the space between the end of the directory data and the end of the cluster. The file slack of the directory node might contain names of previously deleted files, as well as other data.
🗹 Use skipped list — Select this option to reduce wiping time by skipping certain files and folders when wiping files or directory slacks.
The time it takes to wipe files and directory slacks may increase in relation to how many files and folders are on the drive. However, certain files reside on the drive for a longer period of time and are rarely moved, which means that new data is unlikely to be trapped in their file slacks. With that in mind, it might be enough to wipe these type of file slacks once and then configure BCWipe to skip the corresponding files and directories.
If ‘Use skipped list’ is enabled, BCWipe will skip ‘Windows’, ‘Program Files’, and ‘Program Data’ folders by default. Click ‘Edit list’ to add or remove files or folders from the list.
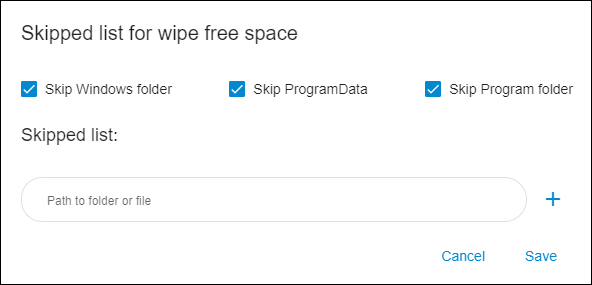
To skip a file or folder when wiping file slacks, type in the path to that file or folder in the edit box under ‘Add folder or file’ and click the ‘+’ icon.
To remove an item from the list, click the cross icon next to it.
When you are finished with configuring the list, click ‘Save’ to apply the changes.
🗹 File names: Select this option to securely overwrite the names and attributes of the files you are erasing.
- For NTFS drives: ‘Master File Table’ (MFT) is a reserved space on NTFS drives where the file system stores the names and attributes of files. Small files may also be stored inside the MFT.
- For FAT/exFAT drives: Directory entries on FAT/exFAT drives contain file names and other attributes.
🗹 NTFS transactions log file: Select this option to eliminate all traces of the files you are erasing.
NTFS is a journaling file system and uses the ‘NTFS Log’ ($LogFile) to record and store temporary data for all the files you are working with. The ‘NTFS transactions log file’ is used to restore the file system in case of a failure.